論文筆記:STGAT - Modeling Spatial-Temporal Interactions for Human Trajectory Prediction
前言
論文連結:STGAT: Modeling Spatial-Temporal Interactionsfor Human Trajectory Prediction
會議:ICCV 2019
Github連結:STGAT
當初學長們在拼投稿paper的時候有幫忙跑過,算是很好implement的一篇,照著readMe一下就跑起來了。Dataset的處理方式幾乎都跟Social GAN一樣。最後拿來跑過heterogeneous的sdd和waymo,表現的其實也很不錯(不過數據都不見光光了哈哈哈),要注意的點大概就是dataset的fps不同吧,要記得調。
用了還算蠻新的Graph Attention Network。
Introduction
S - Spatial
T - Temporal
GAT - Graph Attention Network(GAN已經有人用了)
- Spatial interactions captured by the graph attention mechanism at each time step
- M-LSTM & GAT
- Extra LSTM to encode the temporal correlations of interaction
- G-LSTM
是一篇只聚焦在行人(homogeneous)的研究,先來偷看一下我們的架構圖,等一下再來解釋><
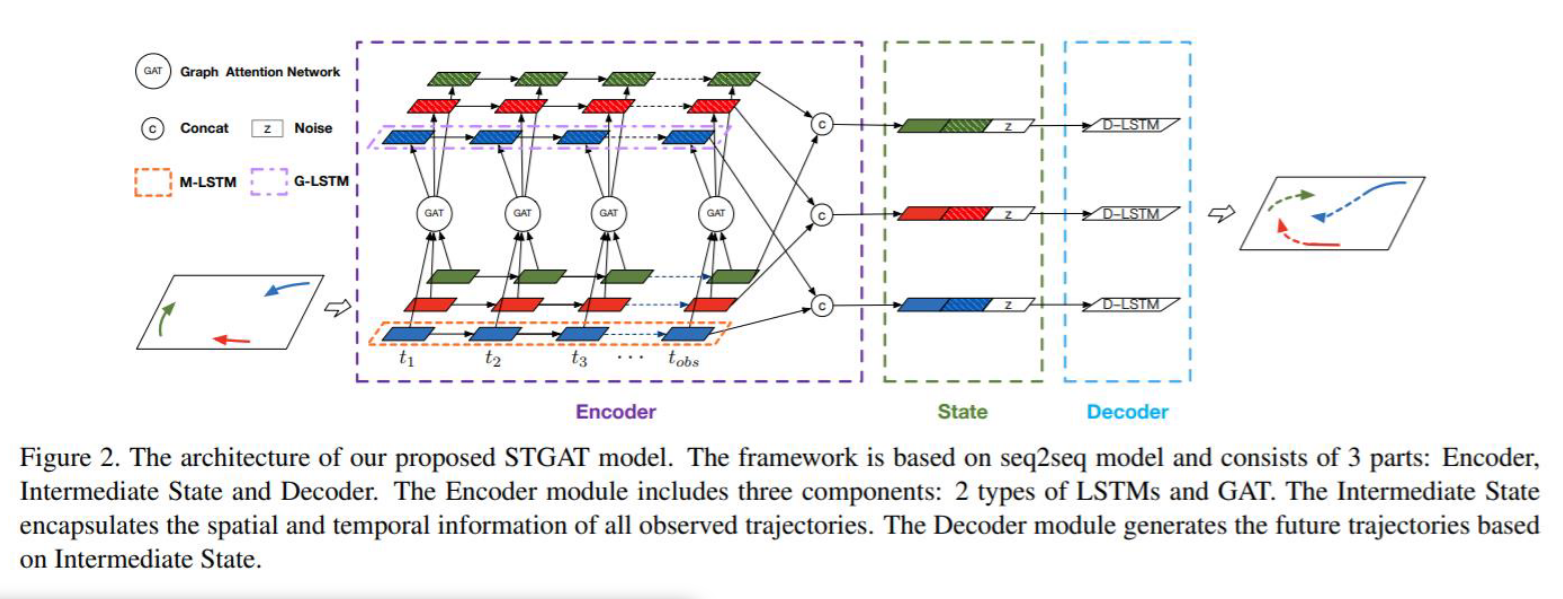
其實簡單來說就是利用相對位置抓一抓移動特徵,再用GAT看看跟誰的關係是重要的,再將這些連同過去的路徑特徵(temporal)一起考慮一下,得到的就是新的相對位置。
Related Works
- LSTM
- 相信大家一定都會><,就不贅述了,具有記憶功能的LSTM在路徑預測這種時序關係強烈的題目中非常重要。
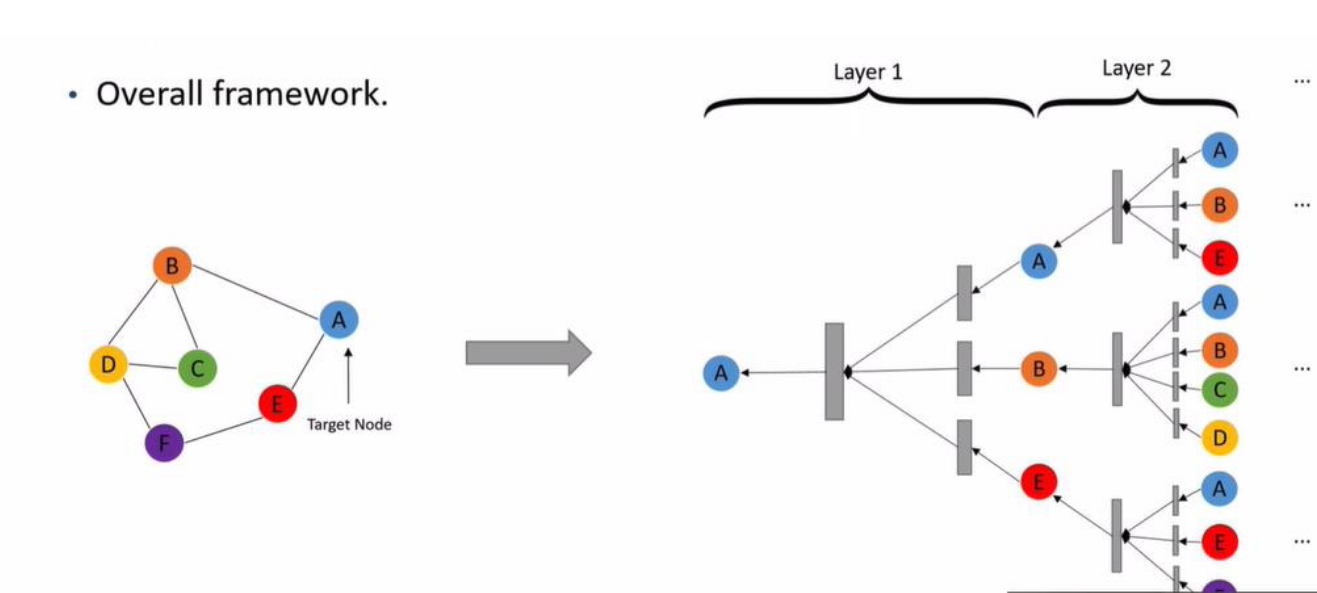
- GAT - Graph Attention Network (ICLR2018)
- 強烈建議看這個影片S6 Presenter: Graph Attention Networks by Zhang Ce,講解的很清楚。
- 以Graph的方式表達關聯,可呈現不規則形狀,相較於CNN等只能以矩形呈現的結構更加有效率。
- 將layer一層一層疊起來,apply不同的權重在相鄰的節點上(specifying different weights to different nodes in a neighborhood)。
- 架構
- 計算方法
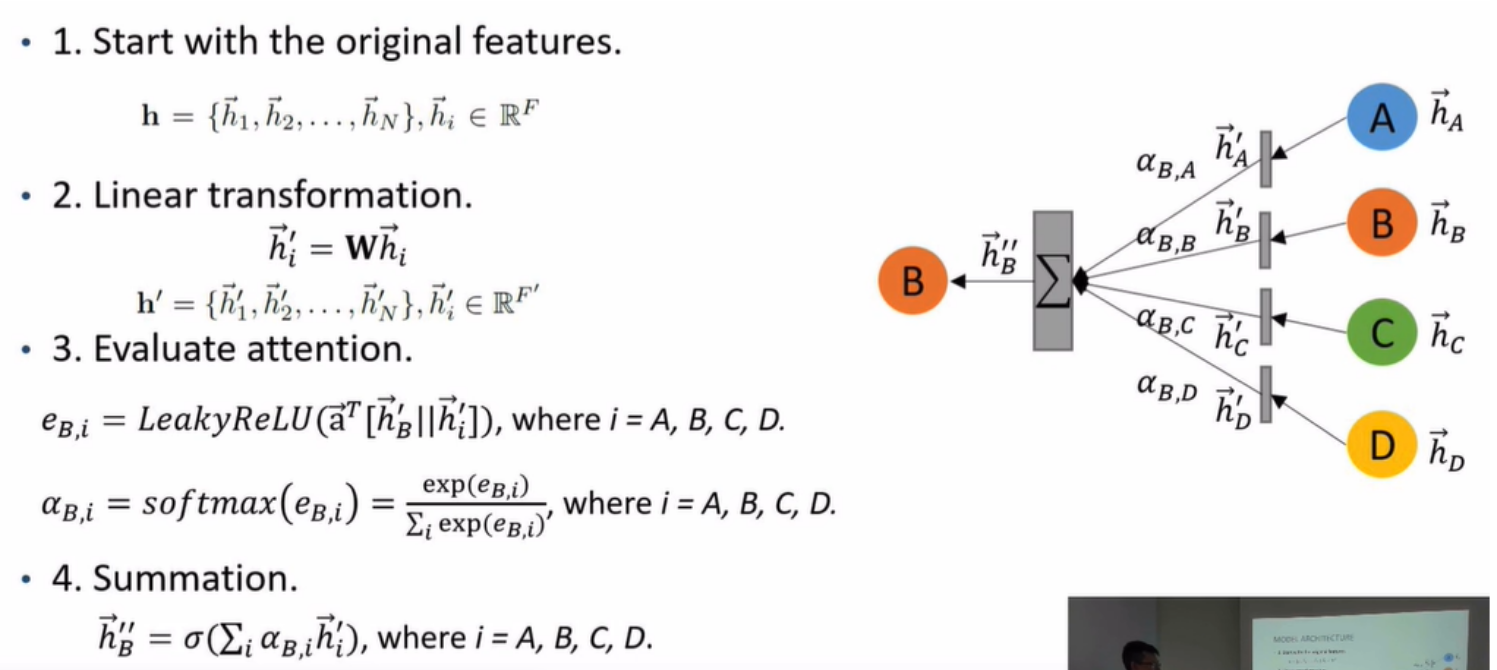
- 以上圖片皆來自影片截圖
- 先排列出該layer的The weight assigned are confusinghidden state,進行一些前處理後,找出所有node與欲求出的node的attention,得以了解哪個nieghbor最為重要(圖中為ABCD與B),如此循環直到所有疊加的layer結束。
- 老實說看完以後不太確定到底為啥要特別用GAT去處理,因為其實感覺一般的Attention就可以處理這些問題了,可能是因為效率比較好(?)
Method
可以參考一下我之前做的簡報優
整體架構

分成三階段
- Encoder : LSTM *2 + GAT
- Intermediate State : encapsulates the spatial and temporal information
- Decoder :generates the future trajectories based on Intermediate State
簡單來說是Encoder/Decoder的結構,把一堆座標、時域、空間特性混在一起(encode)攪一攪,最後解出(decode)一個新的路徑,Social GAN的Generator端也是相同的結構。
Problem Definition
- 直接截圖拉!

步驟
- Encode一個行人
- 將node此刻與前一時刻的x, y做相減,找出相對的移動距離(蠻特別的),放到M-LSTM(motion)中encode。
- GAT-based群眾互動(Crowd Interaction Modeling)
- 以GAT找出與鄰居之間的重要程度(spatial influence from other pedestrians)
- 如圖所示喔喔喔
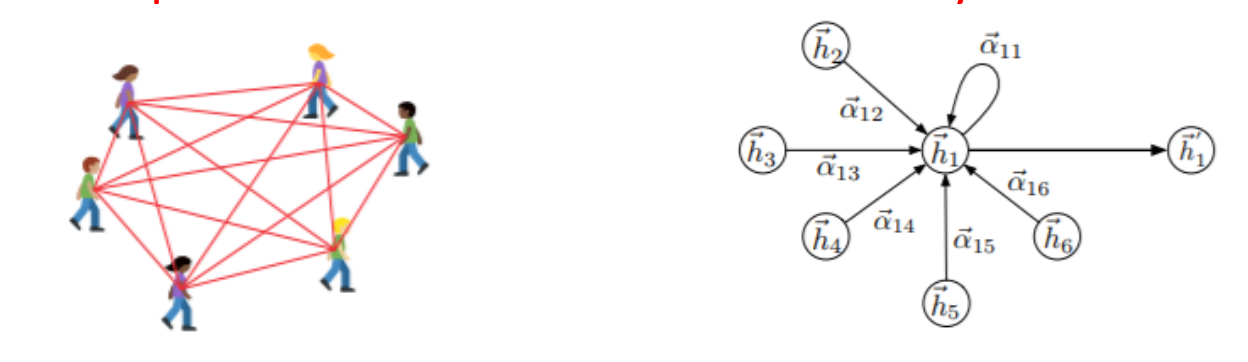
- 再將前面得出的spatial feature丟入G-LSTM,混合時域的特徵(temporal correlation of interactions)
- paper是寫說借此混合空間跟時間的特徵(fusion of spatial and temporal information)
- 將特徵concate(拼起來),包含以下幾個:
- m:spatial特徵
- g:spatial + temporal特徵
- z:在0~1之間normal distribute的noise,是為了製造出不同的路徑
- 以上那些特徵是我們在前面求出來再通過一些embeded function得出來的。
- 最後通過D-LSTM(Decode),預測相對於輸入時刻的移動距離。
Loss Function
- 採用variety loss,由上方步驟中的隨機變數z產生多條路徑,找出loss最短的那個。
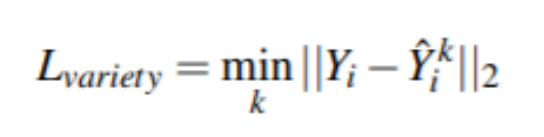
Experiment
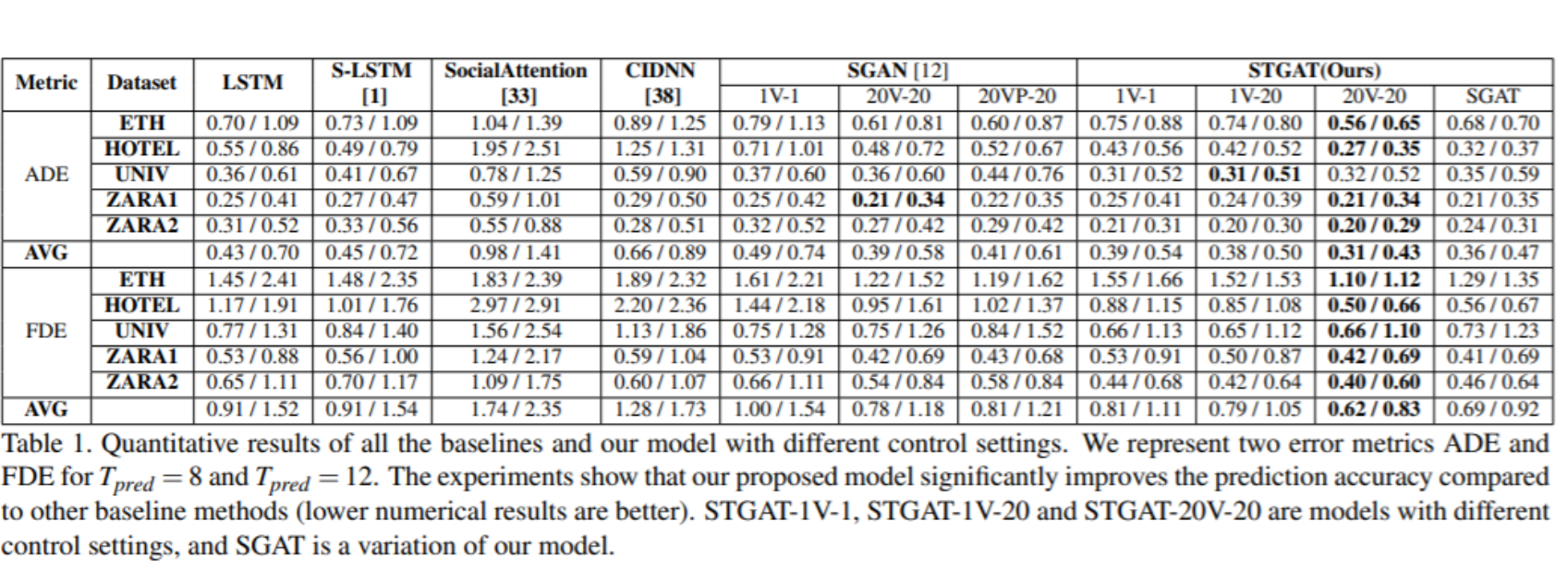
- Performance
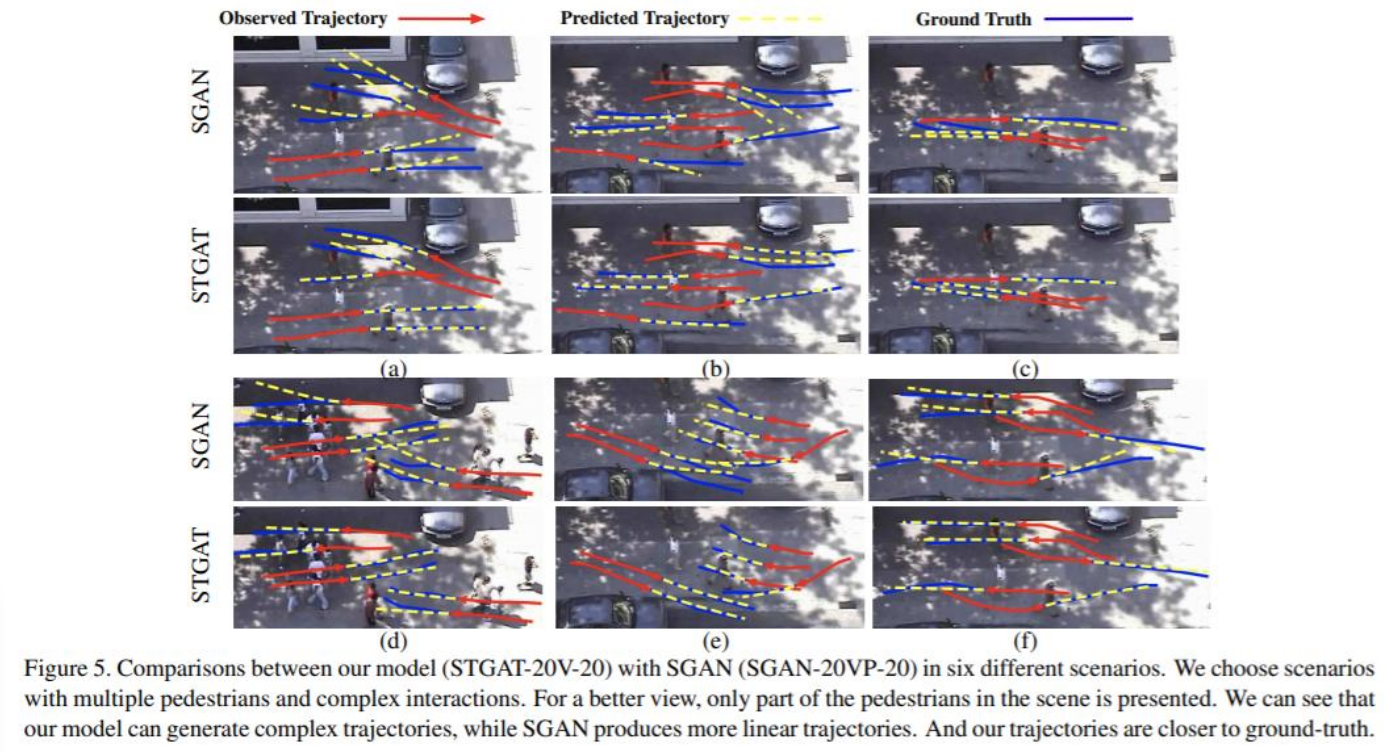
- Compare with Social GAN
結論
- 在ETH & ZARA兩個dataset中表現大幅超越其他model
- novel seq2seq framework
- 根據motion state,利用GAT assign合理的attention給鄰居
缺點
- 常會assign過大的attention給靜止的行人,因為當初是利用相對的移動距離去作為input。
- The weight assigned are confusing。有時會不知道他在assign啥吧,paper裡面說的。
